News | company news | Feb 28,2025
Magnetostrictive displacement sensor current two-wire three-wire four-wire introduction
In magnetostrictive displacement sensors, current output methods usually have two-wire, three-wire, and four-wire configurations. These configurations differ in electrical wiring and signal transmission methods. Depending on the application requirements and installation environment, choosing the right configuration can improve the performance and stability of the system. The following will introduce the characteristics and applicable scenarios of each current output configuration in detail.
1.Two-wire
How it works
In a two-wire system, the power line and signal output line of the sensor are combined into one, and the power supply and signal output are provided through the same pair of lines. This means that the sensor only needs two terminals, one for power input and also as a signal output terminal.
This configuration is simple and quick to wire and is typically used for short distances and simpler applications.
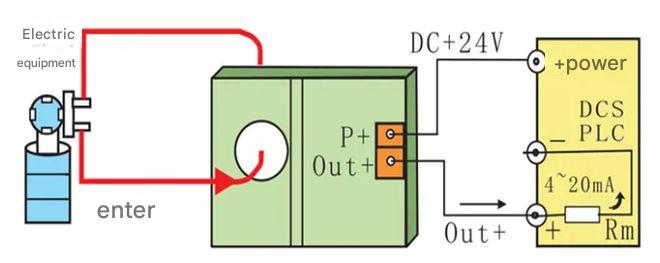
Two-wire magnetostrictive displacement sensor wiring
Features
Power and signal share the same line, reducing wiring complexity, suitable for simple applications and saving wiring space.
Suitable for long-distance transmission and cost-sensitive applications: Due to its simple structure and low cost, it is very suitable for cost-sensitive or simple wiring requirements.
Requires a higher supply voltage: Since the power supply and signal share the same line, there may be a large voltage loss when transmitting the signal, and a higher supply voltage (such as 12-24VDC) is usually required.
No signal ground: Since signal and power lines are shared, signals may be more susceptible to interference, especially over long distances or in electrically noisy environments.
Applicable scenarios
It is suitable for occasions that require simple wiring, such as short-distance transmission, applications with low precision requirements, or occasions where equipment installation space is limited.
2.Three-wire
How it works
In a three-wire configuration, the sensor uses three wires for power and signal transmission: a power line (+VDC), a ground line (GND), and an output signal line (usually a current output signal).
The power line provides power to the sensor, the ground line ensures a common reference for the signal and power, and the output signal line transmits the displacement data from the sensor.
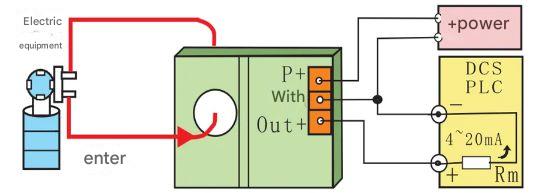
Three-wire magnetostrictive displacement sensor wiring
Features
Lower voltage loss: Compared with the two-wire system, the three-wire system provides an independent ground wire, which can reduce voltage loss and ensure signal quality.
Suitable for medium distance and high precision applications: The three-wire system provides more stable signal transmission than the two-wire system and is suitable for applications requiring higher accuracy and stability.
Less signal interference: Due to the independent grounding wire, the signal interference caused by power supply noise can be reduced, which is suitable for some environments with high requirements on signal quality.
Applicable scenarios
It is used in medium-distance transmission applications, especially in environments that require precise signals and stable outputs, such as in industrial automation control systems, where the distance between the sensor and the control system is not far but high signal quality is required.
3.Four-wire
How it works
The four-wire configuration is the most complex, using four separate wires: one for power (+VDC), one for ground (GND), one for the signal output, and one for the ground loop (usually the signal return).
This method transmits the signal output and loop through two independent wires, which can effectively isolate the signal and power supply parts, reduce interference, and ensure high signal accuracy.
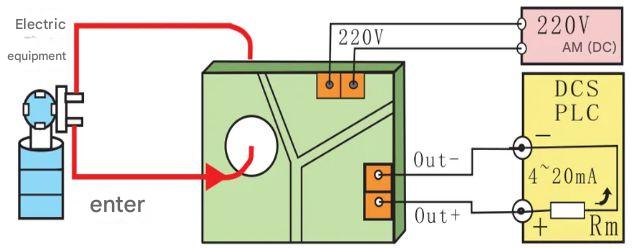
Four-wire magnetostrictive displacement sensor wiring
Features
Minimum signal loss and interference: Since the signal and power are completely separated, the current loop and the power loop are transmitted independently, minimizing noise interference.
Best effect over long distances: The four-wire system is suitable for long-distance transmission and high-precision measurement, ensuring that signal quality will not be attenuated due to long transmission distances.
Best for complex and high-precision applications: This configuration provides the most stable signal and is suitable for applications requiring high-precision, complex control.
Applicable scenarios
It is suitable for long-distance transmission and highly accurate industrial automation control systems, especially in high electrical noise environments such as power equipment, heavy machinery, robots, etc.
Comparison Summary
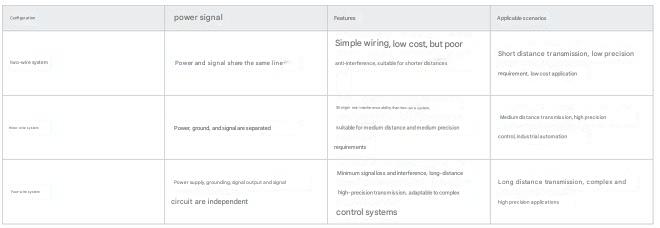
Comparison of two-wire, three-wire and four-wire current of magnetostrictive displacement sensor
Summarize
Two-wire system: suitable for low-cost and simple applications, but the transmission distance and anti-interference ability are limited.
Three-wire system: suitable for medium precision and medium distance applications, with good signal stability and anti-interference ability.
Four-wire system: suitable for high-precision and long-distance applications, providing optimal signal quality and minimal interference, suitable for complex and high-demand industrial automation control systems.
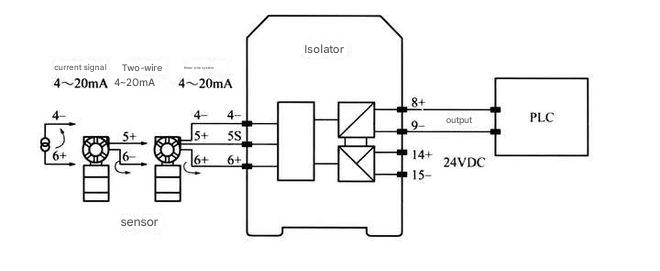
Current magnetostrictive displacement sensor and PLC wiring
According to application requirements, selecting the appropriate current output method can ensure that the magnetostrictive displacement sensor provides stable and accurate measurement signals in different environments and conditions.
--- END ---

Feb 04, 2026
Why is single‑phase window type current transformer so popular in the South American electricity market? —Technical Analysis Based on the South American Power Bureau’s Bidding and Outdoor Environment In countries, like Brazil, Chile, Peru and Colombia the power infrastructure construction has kept growing in recent years. The distribution network upgrades, the energy grid integration and the… Continue reading Why single‑phase window type current transformer Dominate South America’s Power Grid

Feb 03, 2026
Why have single phase satuation current transformers (CTs) become an essential core component of switchgear in Southeast Asia? — Detailed technical analysis using the ICT series encapsulated transformer as an example. We examine the ICT series encapsulated transformer. In Asian countries such, as Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand and Vietnam the low-voltage switchgear appears a lot in… Continue reading Why Single-Phase Saturation Isolation Current Transformers Are Essential in Switchgear

Jan 22, 2026
People use Current transmitter. Why do people use transmitters, in the chillers the air compressors, the generators and the IoT systems? In systems I see chillers, in commercial buildings air compressors in factories and generators, in data centers. The chillers, the air compressors and the generators all have one thing in common. In short devices… Continue reading Why Current Transmitter Matter in Chiller, Air Compressor, and Generator