News | company news | Nov 22,2024
What are the functions of IoT devices using current transformers
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming every industry, bringing previously unimaginable cost-effectiveness with unprecedented levels of automation, intelligence, and connectivity. Let’s take IoT devices as an example of how our world is becoming more connected. First, what products and applications are connected by IoT devices, and why?
In the consumer sector, we see many different home automation applications, such as smart thermostats, connected doorbells, smart coffee pots, and connected refrigerators, which are changing the way consumers think about and interact with their personal infrastructure.
However, it is in the commercial and industrial sectors that IoT has the greatest impact. Our goals are: to improve efficiency, accuracy, safety and security, and to provide data, reports, alerts, and insights.
In the energy and industrial sectors, we see smart meters, remote tank monitoring, and electric vehicle charging stations. Smart cities are deploying IoT to create connected lighting, traffic management systems, and intelligent transportation systems. Precision agriculture is bringing higher crop yields and lower costs, and improved efficiency, which will have a profound impact on agricultural production. Positive impact on the environment . And in the retail sector, IoT is significantly improving the functions of everything from smart ATM to digital signage and kiosks.
When it comes to IoT hardware and connectivity (the underlying infrastructure that makes the Internet of Things a reality), Digi provides key IoT devices for your application development or works closely with key vendors. Examples of IoT devices we will discuss in this blog include the following:
Sensors ( current transformers ) Radio equipment
System on Modules (SOM) and Single Board Computers (SBC)
Gateway
Cellular routers
Additionally, we will discuss another important aspect of building wireless applications with IoT devices: enterprise device management software, which provides the central monitoring, management, and decision-making insights needed to effectively monitor a network of deployed devices. Digi provides enterprise-grade software to manage a broad portfolio of devices and components, improve uptime, and increase security.
In IoT devices and applications, sensors act as the “eyes and ears” of devices in a variety of use cases from oil and gas to agriculture, commercial and industrial metering, industrial tanks, municipal sewage systems, security systems, etc. Various components from Digi partners can monitor and capture environmental data including motion, temperature, humidity, volume, pressure, flow, acceleration, sound, light, etc. Basically anything that moves or fluctuates in some way can be monitored and captured.
The sensor converts the detection result into a human-readable format, which is displayed at the sensor location or transmits the data to a central server for reading or further processing. In many cases, the sensor report will start a process. This can be anything from managing water flow, turning on a fan or irrigation system, or sending an alarm.
When you are selecting a sensor for your IoT application, some key factors to consider include accuracy, environmental conditions, temperature/humidity operating conditions, range (upper and lower limits), calibration, and cost. The sensor must be designed to withstand the environment in which it will be installed. This is a key consideration as many sensors operate in harsh outdoor environments and often must function optimally 24/7.
RF modules can send signals wirelessly between two devices that have a transmitter and a receiver installed. RF modules are ideal for many applications for several reasons:
Related blog post: How do IoT devices communicate?
Electronic radio design is notoriously complex due to the sensitivity of radio circuits and the precision of components and layout required for specific frequencies.
In addition, you must carefully monitor the manufacturing process to ensure that RF performance is not adversely affected. Radio circuits are often subject to radiated emission limits, which require compliance testing and certification by standards organizations such as ETSI or the Federal Communications Commission (FCC).
For these reasons, many design engineers find it easier to “plug in” a pre-made, pre-certified RF module rather than attempt an independent design, saving development time and money.
RF modules are commonly used in consumer applications such as garage door openers, wireless alarm/monitoring systems, and industrial remote control and smart sensor applications. Because RF modules do not require line of sight for operation, they are increasingly replacing older infrared communication applications.
The most common frequencies used in commercially available RF modules are the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) radio bands (such as 433.92 MHz, 915 MHz, and 2.4 MHz). These frequencies are used because national and international regulations govern the use of radios for communications. Short-range devices can also use frequencies in the unlicensed spectrum, such as 315 MHz and 868 MHz.
RF modules may conform to a defined RF communication protocol, such as Zigbee, Bluetooth Low Energy, or Wi-Fi, or they may implement a proprietary protocol. Although cellular radios operate in a similar manner, unlike RF modules, which connect directly to cell towers for communication, RF modules require a gateway to interact with the outside world (the Internet).
System-on-module (SOM) integrates system functions into a single module, bringing simplicity and intelligence to embedded IoT systems.
For IoT applications, integrated wireless connectivity (including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular connectivity) can be widely deployed in a variety of scenarios. In addition, low power consumption is also a priority. A significant advantage of SOM is that it reduces the time and cost of developing PCB-based designs. SOM offers excellent design reusability and can be integrated into many embedded computer applications.
A single-board computer (SBC) is an entire computer built on a single circuit board, including a microprocessor, memory, input/output, and connections. Unlike desktop PCs, SBCs typically do not have expansion slots. Digi SBC relies on NXP microprocessors to provide pre-certified Wi-Fi and Bluetooth connectivity, superior power management and enterprise-grade security.
Selecting the right product for your application is an important evaluation process. During the evaluation and prototyping phase, development teams often start with a single-board computer and then select a SOM for the final design that meets the form factor, connectivity, and performance requirements of the end application. Some important factors include the development environment and the availability of supporting libraries and documentation. For example, Digi system-on-modules and SBCs are built on open source operating systems and have supporting libraries and documentation to help drive rapid prototyping and development, ensuring fast time to market.

A gateway is an IoT device that is the connection point between the Internet (the cloud) and controllers, sensors, and other IoT hardware. All data transmitted to the cloud passes through a gateway, which can be a dedicated hardware device or a software program.
With IoT applications, sensors can generate thousands of data points per second. The gateway processes this data locally before sending it to the cloud, minimizing the amount of data that needs to be forwarded. As a result, response times and network costs are significantly improved.
IoT gateways can also provide additional security to IoT networks and the data they transmit. Because an IoT gateway can manage information in both directions, it prevents data leakage and protects IoT devices from compromise through tamper detection, encryption, hardware random number generators, and encryption engines.
Gateways can operate in a variety of situations, from temperature-managed indoor installations to remote outdoor installations. When the application requires the gateway to operate in a harsh environment, it is important to select a gateway with a rugged enclosure that is designed to withstand environmental factors such as extreme temperatures, moisture, and vibration.
Cellular routers provide shared Internet access through a cellular gateway. A standard wireless interface allows network-enabled devices to easily share a connection. Cellular routers access the Internet through cell towers.
Without a wired connection, cellular routers can create an Internet gateway on the move (such as on a moving train) or in areas without landlines, or as a failover for backup connections.
Today, with cellular routers are possible to install cellular routers with integrated Band 14 capabilities to provide preemptive cellular communications to first responders and
extended primary users during emergencies or catastrophic events .
Routers are used for a wide range of purposes, from simple data routing for small networks to preemptive emergency communications for first responders. Routers are used both inside and outside in harsh environments such as temperature fluctuations, moisture, vibration, and other environmental factors. Routers
also have a variety of functions depending on the connectivity needs, whether the communication is from a fixed or mobile point, application requirements for security, communication partitioning, cellular connectivity to multiple carriers, and failover requirements for business use cases. To
help customers evaluate the right router for their application, Digi has classified cellular routers into three different categories:
When it comes to cellular communications hardware, the first device to tackle is the modem, which is basically a “dumb” device – neither smart nor programmable. The modem simply sends traffic from point A to point B without any operation or data protection. In contrast, a router or extender is a highly intelligent device. In fact, every Digi router includes a cellular modem, and most Digi routers even support dual SIM cards from multiple cellular carriers.
A quality router should also offer a powerful firewall to handle packet-level traffic inspection, coordinate incoming traffic and outgoing requests, and support multiple types of data security tunneling options such as IPSec, GRE, L2TP, PPTP or even OpenVPN. Many industrial-grade cellular routers include input/output or I/O options to handle simple operations on field devices, such as shutting down an overheating pump.
Cellular gateways don’t have the same network traffic control capabilities as routers, but they can often simplify configuration. Gateways often have onboard programming models or simple control options. As the name suggests, gateways provide protocol conversion. Therefore, it can convert Zigbee, wired hardware or Modbus to cellular technology or even other technologies. There are many options when it comes to cellular gateways.
Related blog post: Cellular Routers, Extenders, and Gateways: What’s the Difference?
For an IoT solution to meet your needs, you must have enterprise device management software to successfully deploy and manage devices. Once deployed, you may not be able to physically access the devices, or the scale of the deployment makes it impractical to manually manage the devices. Enterprise management software, such as Digi Remote Manager(Digi RM), enables your team to successfully advance projects from proof of concept all the way to deployment and manage the devices long-term after they reach their final location.
IoT devices often must be updated with configuration, functionality, and security to meet current business needs. The right management solution allows administrators to quickly and securely change configurations, update firmware, or push security patches to IoT devices. The software allows you to access data from IoT devices from anywhere, whether in your home office or in the field, and integrate that data into your own cloud platform.
Enterprise device management software, such as DRM, also allows you to easily get detailed reports and real-time alerts on network health and device status via text, email, or internal management software, which may have been overlooked before.
There is no one-size-fits-all approach when designing an IoT device deployment. The following diagram shows an example of IoT devices in an Industrial IoT (IIoT) use case, where data is collected from multiple points and then routed through cellular IoT devices to the cloud, where the information can be accessed and managed by various devices and end-user applications.
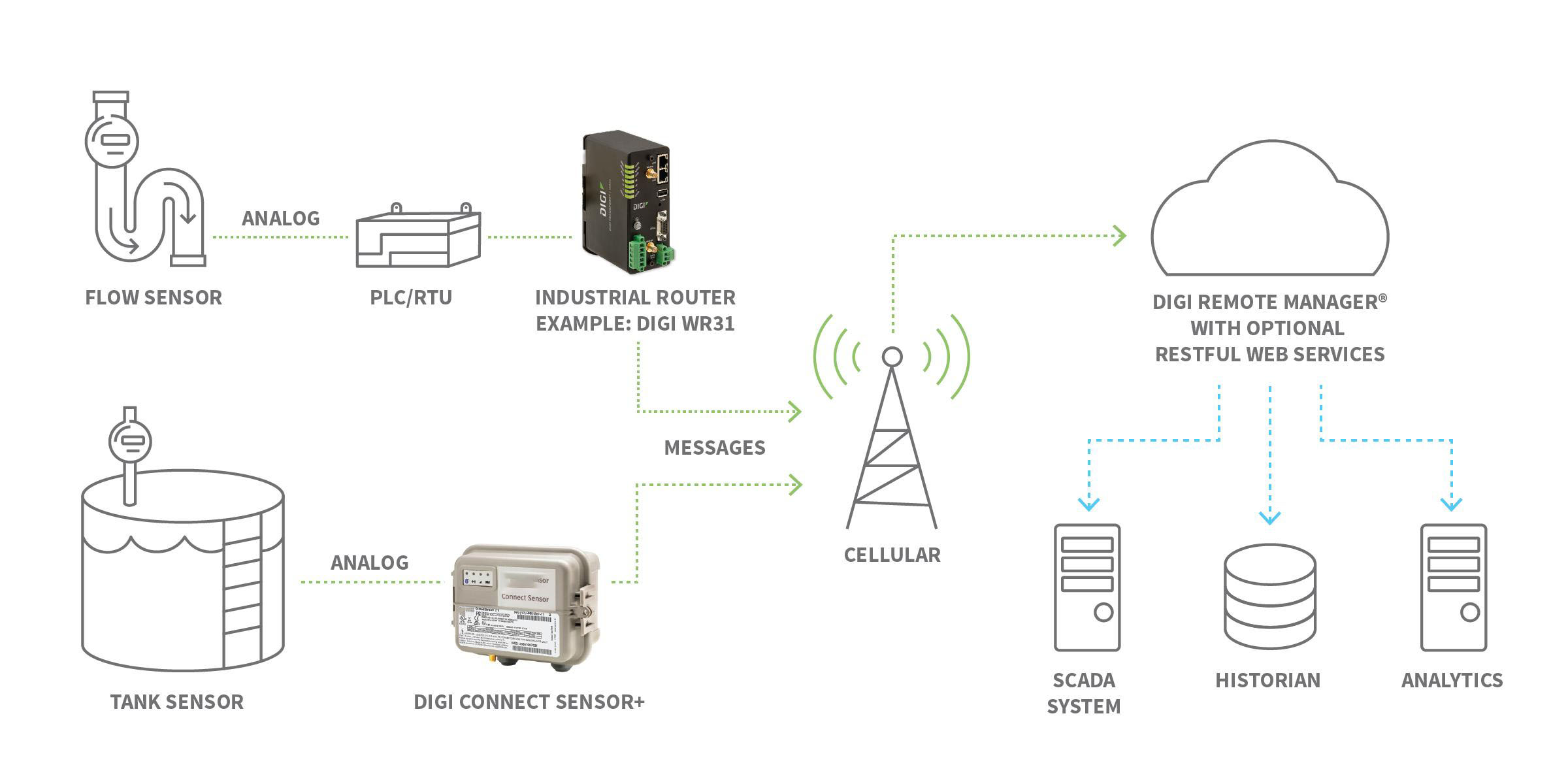
Perhaps the best way to understand the power and scope of IoT is to look at how leading companies are applying IoT hardware to bring greater intelligence, speed, and connectivity to small spaces and far-flung places. Here are some use cases that illustrate how IoT can help your organization increase efficiency and improve processes.
Read about these and other projects in the
IoT is revolutionizing numerous markets in the South Korea and around the world. In markets such as energy, smart cities, healthcare, industrial, retail, or transportation, IoT devices are key to gaining advantages such as automation, efficiency, intelligence, data metrics, and connectivity and communication to keep up with and surpass competitors.
In today’s market, as technology advances and devices become more powerful and affordable, disruption is easier and can quickly spread across a wide range of market segments. IoT. For example, companies such as Progressive and Redbox have leveraged new technologies in IoT to surpass once-untouchable players such as Allstate and Blockbuster.
When it comes to IoT hardware, HEYI is your partner and facilitator for all things IoT. We have a complete portfolio to help you meet new challenges in your business, and we have the long-term expertise to help you navigate the process using any and all of the IoT products mentioned above.
--- END ---

Dec 23, 2025
Switch position indicators are parts of systems. In my work I have seen switch position indicators, in power plants, substations and industrial control cabinets. Switch position indicators show the status of a switch from a distance. There are two kinds of switch position indicators: switch position indicators and electronic (LED) switch position indicators. Each kind… Continue reading How to Choose Mechanical and Electronic Switch Position Indicator

Dec 22, 2025
Cómo seleccionar correctamente transformadores de corriente para exteriores en Sudamérica: ejemplos de RECT y OCT de HEYI Electric En la construcción y operación de sistemas eléctricos en Sudamérica, la elección del transformador de corriente para exteriores es fundamental. Trabajo en un proyecto eléctrico. Busco un transformador de corriente que aumente la seguridad de los equipos.… Continue reading Cómo seleccionar transformadores de corriente para exteriores en

Dec 18, 2025
HEYI Electric: Providing complete solutions for power engineering projects in Malaysia, from current monitoring to status indication. The biggest challenge, for companies in Malaysias power sector is keeping the system reliable and making monitoring easy. HEYI Electric offers more, than measurement products. HEYI gives a set that includes precision current transformers, flexible current transmitters and… Continue reading Position indicator switch is used to create solutions for Malaysia.