News | company news | Oct 14,2024
Introduction
In order to make full use of the alarm information in the operation of power system components, this paper makes full use of conditional probability tools, taking parallel high-voltage reactors as an example, to establish the correlation between electrical analog measurement results and data alarm signals. By fitting the correlation function and using it in data mining methods such as outlier detection, online monitoring of component operating status is achieved.
Background
Overcurrent is an abnormal condition that often occurs during the operation of high-voltage shunt reactors, which can easily cause component heating and shorten the life of the equipment. In order to avoid long-term overcurrent, the substation site often needs to be equipped with a reactor overcurrent monitoring device to identify overcurrent conditions.
However, in actual operation, it was found that due to the harsh operating environment of the reactor’s current transformer (CT), abnormal secondary side measurement failures occurred from time to time as the operating time increased, resulting in frequent false alarms from the overcurrent alarm device, misleading on-site operation and maintenance personnel. Therefore, a method for determining the correctness of high-voltage reactor overcurrent alarms based on SCADA operation data is urgently needed to provide auxiliary decision-making for on-site operators.
Methods and innovations
In order to solve the problem that the high-voltage reactor current cannot be directly measured in the actual system and can only be indirectly expressed through the overcurrent alarm, this paper uses the idea of conditional probability to construct the correlation between the effective value of the bus voltage and the reactor overcurrent alarm, as shown in Figure 1. At the same time, the Sigmoid function is used to fit this relationship.
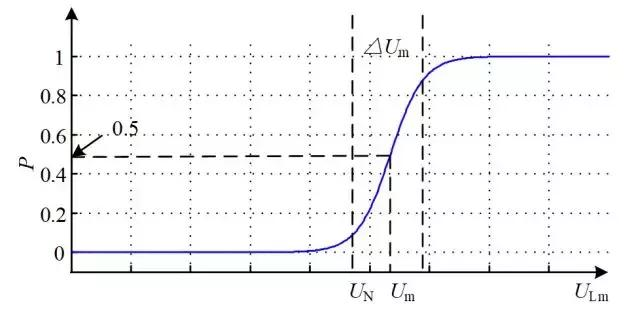
Figure 1 Correlation between bus voltage RMS value and reactor overcurrent alarm
In order to realize the correct identification of overcurrent alarm, the function center point and uncertainty domain are selected as characteristic indicators to form a two-dimensional key characteristic data point (KCDP) for fault diagnosis.
Taking into account the fact that it is difficult to collect a lot of abnormal data during the actual operation of the power system, this paper proposes a method of defining the normal domain of feature data based on normal operating data, and then using the outlier detection method to determine the distance between the detection point and the normal domain, generate relevant criteria, and perform fault diagnosis. The schematic diagram is shown in Figure 2.
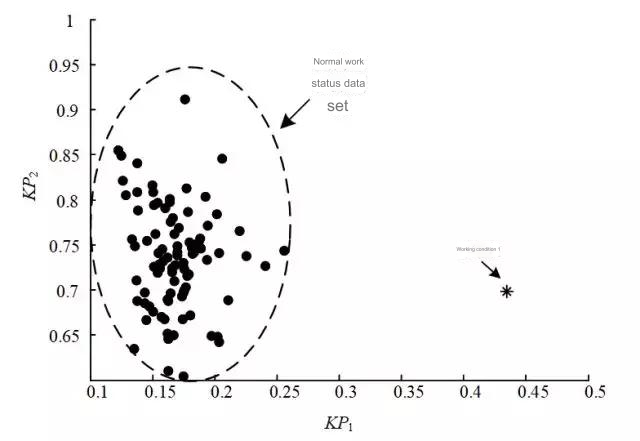
Figure 2 Diagnosis dataset
The specific approach is as follows: multiple key feature data points obtained under normal working conditions and key feature data points on the detection day constitute a diagnostic data set, and outlier detection is performed on them using the isolation forest outlier detection algorithm, and the anomaly score of each key feature data point in the set is calculated. Assuming that the anomaly score of the key feature data points under normal working conditions satisfies the Weibull distribution, the diagnostic criterion for abnormal faults in the current transformer measurement of the high-voltage shunt reactor body is given based on the confidence interval of the distribution.
In conclusion
This paper proposes an online diagnosis method for abnormal faults in current transformer measurement of high-voltage shunt reactor body based on outlier detection.
This method uses the conditional probability relationship of the high-voltage shunt reactor monitoring system sending an overcurrent alarm signal under the condition of a specific bus voltage effective value to obtain the key characteristic indicators of the main current transformer fault diagnosis. The generation of the above two key characteristic indicators does not require the acquisition of current transformer measurement results, which solves the problem that the current transformer measurement value cannot be directly obtained and can only be indirectly characterized by overcurrent alarms.
At the same time, this method selects two physical quantities, the center point offset of the P-ULM curve and the uncertainty domain of the P-ULM curve, as key indicators for judging overcurrent false alarms. Analysis shows that once the measurement accuracy of the current transformer in the system changes significantly, the above two physical quantities can better reflect the abnormal measurement of the current transformer and provide a basis for fault diagnosis.
Finally, the method uses the isolation forest algorithm to detect outliers in the diagnostic data set and gives the fault diagnosis criteria. The simulation results verify the effectiveness of the method. The method is easy to implement and does not require additional measurement equipment. The case test was carried out based on the actual engineering system and achieved good results, which has good practicality.
--- END ---

Dec 26, 2025
Application of CT clamp meter transformer in high-voltage power distribution systems —Taking HEYI CT clamp meter transformer as an example In high voltage power distribution systems I use measurement I use operation monitoring and I use fault early warning to keep the power grid safe and stable. As power distribution systems become smarter and run… Continue reading Application and Advantage of CT clamp meter transformer

Dec 23, 2025
Switch position indicators are parts of systems. In my work I have seen switch position indicators, in power plants, substations and industrial control cabinets. Switch position indicators show the status of a switch from a distance. There are two kinds of switch position indicators: switch position indicators and electronic (LED) switch position indicators. Each kind… Continue reading How to Choose Mechanical and Electronic Switch Position Indicator

Dec 22, 2025
Cómo seleccionar correctamente transformadores de corriente para exteriores en Sudamérica: ejemplos de RECT y OCT de HEYI Electric En la construcción y operación de sistemas eléctricos en Sudamérica, la elección del transformador de corriente para exteriores es fundamental. Trabajo en un proyecto eléctrico. Busco un transformador de corriente que aumente la seguridad de los equipos.… Continue reading Cómo seleccionar transformadores de corriente para exteriores en