News | company news | Sep 21,2024
Selection of residual current protector in charging pile
With the explosive growth of the number of new energy vehicles in the past two years, the construction scale of its supporting facilities charging piles has also expanded. In the seven years from 2010 to 2017, the number of charging piles in China has increased from more than 1,000 to 210,000
With the explosive growth of the number of new energy vehicles in the past two years, the construction scale of its supporting facilities charging piles has also expanded. In the seven years from 2010 to 2017, the number of charging piles in China has increased from more than 1,000 to 210,000. The growth of the new energy vehicle market cannot be separated from the construction of basic charging facilities. How to ensure the safety of electricity in the charging process, especially to prevent the leakage of current from causing harm to life and property, is a problem worthy of attention.
Residual Current Operated Protective Devices (RCD) are widely used in low-voltage power distribution systems to prevent electric shock accidents, electrical equipment leakage damage, and electrical fires. Also in the field of electric vehicle charging, RCD is also widely used as a basic electrical protection device.
There are four modes of electric vehicle charging, which are clearly described in GB/T 18487.1-2015 “Electric Vehicle conduction Charging System Part 1: General Requirements”. Mode 1 uses a charging connection cable to connect electric vehicles to the AC grid. Residual current protection mainly relies on residual current protection devices (RCDS) in the building distribution box. Since it is not guaranteed that all existing building installations are equipped with RCDS, this method is very dangerous and has been banned. In mode 2, the cable control protection device (IC-CPD) is installed on the charging connection cable, and the IC-CPD has the residual current detection protection function; Mode 3 uses special power supply equipment to directly connect the electric vehicle to the AC power grid, and a control guidance device is installed on the special power supply equipment, namely AC charging pile; Mode 4 When the electric vehicle is connected to the AC or DC power grid, a DC power supply device with control guidance function is used, that is, a DC charging pile. Here, we mainly discuss the selection of residual current protectors in mode 3 and Mode 4 charging piles.
According to the requirements of GB/T 18487.1-2015, the residual current protector of AC power supply equipment should be type A or Type B, which meets the relevant requirements of GB 14084.2-2008, GB 16916.1-2014 and GB 22794-2008. FIG. 1 shows the schematic diagram of the control guidance circuit for charging mode 3. A residual current protector is installed inside the power supply device.
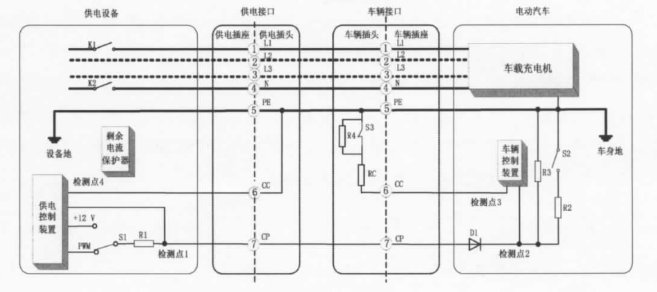
FIG. 1 Schematic diagram of charge mode 3 control guidance circuit
What is A Type A or B residual current protector? China’s residual current protection device (RCD) guiding standard GB/Z 6829-2008 (IEC/TR 60755:2008,MOD) “General requirements for residual current action protectors” from the basic structure of the product, residual current type, trip mode and other aspects are divided. According to the type of residual current, RCD can be divided into AC type, A type and B type. AC type residual current protector: RCD that ensures trip against sudden application or slow rise of residual sinusoidal AC current. Type A residual current protector: An RCD that incorporates the characteristics of type AC and superposition the pulsating DC residual current and the pulsating DC residual current with 6mA smooth residual current to ensure trip. Type B residual current protector: contains the protection characteristics of type A. In addition, it can also ensure the tripping RCD of sinusoidal AC residual current, AC residual current superposition smooth DC residual current, pulsating DC residual current superposition smooth DC residual current, pulsating DC residual current generated by two-phase or multiphase rectifier circuit, smooth DC residual current.

FIG. 2 Internal structure of AC charging pile
At present, because the price of type B RCD is too expensive, most of the domestic AC charging piles are installed inside the type A residual current protector. The following figure shows the internal structure of the AC charging pile, which uses A type A residual current protection device.
So can the residual current protector of type A meet the leakage protection requirements of charging piles? Let’s analyze the type of residual current that can be generated during charging.

FIG. 3 Schematic diagram of connection between electric vehicle charging facilities, power grid and electric workshop
As shown in Figure 3, in the process of using AC charging piles, AC charging piles and vehicle couplers are connected to the public power grid. If the insulation inside the piles is damaged, power-frequency AC leakage current may be generated. In the electric vehicle part, the leakage current that may be generated mainly comes from the leakage of the vehicle charger, and the general topology of the charger is mainly AC/DC and DC/DC. The following figure shows the main circuit diagram of a common vehicle charger.

Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the main circuit of a vehicle charger
The AC/DC part of the single-phase input AC is first filtered by EMI, and then under the action of the Boost APFC circuit, the 85~265V AC is rectified into a stable output DC 400V voltage, and provides DC input for the later stage. The DC/DC part uses the phase-shifted full-bridge LLC main circuit to convert the DC voltage of 400V into the acceptable voltage of the battery. When the insulation between the circuit board and the device housing is damaged, the fluctuating DC residual current may be generated in the rectification part, and the DC residual current with a small ripple coefficient may be generated in the Boost APFC circuit. Bender’s figure is used here to explain in detail the generation and harm of DC residual current.

Figure 5 DC leakage generation of isolated charger
It can be seen that DC leakage may occur in the DC/DC part of the push-pull full bridge converter, China’s low-voltage distribution system generally uses TN power supply, the equipment metal shell is connected to the working neutral line, DC leakage will feed back to the charging line through the body and PE line, affecting the current waveform of the entire system. Through the simulation of the equivalent circuit, it is found that the current waveform of the whole system will change, as shown in the figure below.

Figure 6 Current waveform of DC fault system of charger
It can be seen that after DC leakage occurs at the back end, it will also affect the front circuit, and the pulsating DC waveform after rectification will be distorted, resulting in spikes, which will interfere with the back-end circuit step by step, affecting the charging effect and even affecting the battery life. On the other hand, due to the existence of the TN system, this fault will not form a large voltage in the body, which is less harmful to the human body, but if the ground wire of the connected system is missing or the PE line is disconnected, then this part of the voltage will hurt the human body. In fact, many places in the country, especially in rural areas, there are problems in the connection of PE wire ground lines. The existing type A RCD can only detect pulsating DC leakage without interference from DC 6mA current, but can not detect DC leakage and disconnect protection, when DC leakage is greater than 6mA, due to the DC residual current will cause the magnetic core pre-magnetization, so that the trip value increases, resulting in type A RCD can not operate normally, so it must use type B RCD for protection!
Similarly, inside the DC charging pile, the mains electricity is converted into high-precision DC electricity to charge the battery through the non-vehicle charger. The leakage protection of DC charging pile is divided into AC side and DC side. Theoretically, type B RCD should be added to the AC side for protection, and DC side should be equipped with DC ground insulation monitoring device to detect the DC positive and negative electrode ground insulation detection.
In the foreseeable future, as new energy vehicles enter thousands of households, charging piles will become an indispensable part of people’s lives, therefore, the replacement of the residual current protector in the charging pile is very necessary, only a safe electricity environment can let everyone rest assured to enjoy the convenience brought by new energy vehicles.
Magtron’s overall SoC chip solution based on iFluxgate technology is A digital integration for type B leakage protection, and provides a set of cost-effective type B leakage solution for RCCB to upgrade from the traditional AC /A type to B type technology, providing a better guarantee for the power safety of charging equipment.
--- END ---

Feb 04, 2026
Why is single‑phase window type current transformer so popular in the South American electricity market? —Technical Analysis Based on the South American Power Bureau’s Bidding and Outdoor Environment In countries, like Brazil, Chile, Peru and Colombia the power infrastructure construction has kept growing in recent years. The distribution network upgrades, the energy grid integration and the… Continue reading Why single‑phase window type current transformer Dominate South America’s Power Grid

Feb 03, 2026
Why have single phase satuation current transformers (CTs) become an essential core component of switchgear in Southeast Asia? — Detailed technical analysis using the ICT series encapsulated transformer as an example. We examine the ICT series encapsulated transformer. In Asian countries such, as Malaysia, Indonesia, Thailand and Vietnam the low-voltage switchgear appears a lot in… Continue reading Why Single-Phase Saturation Isolation Current Transformers Are Essential in Switchgear

Jan 22, 2026
People use Current transmitter. Why do people use transmitters, in the chillers the air compressors, the generators and the IoT systems? In systems I see chillers, in commercial buildings air compressors in factories and generators, in data centers. The chillers, the air compressors and the generators all have one thing in common. In short devices… Continue reading Why Current Transmitter Matter in Chiller, Air Compressor, and Generator